Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-03-17 Origin: Site








CNC machines are essential in today’s manufacturing world, but how many axes can a CNC have? The number of axes affects precision, complexity, and speed.
In this post, we’ll explain how different CNC axes influence machining capabilities. You’ll learn how more axes improve accuracy and flexibility, helping you
choose the right machine for your needs.
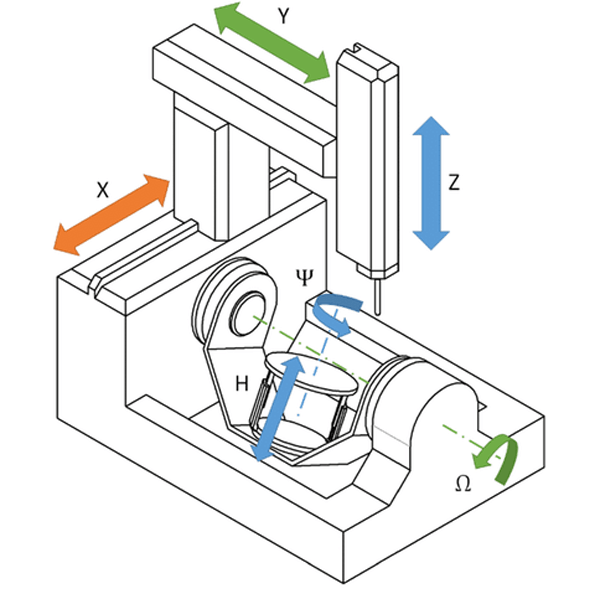
In CNC machining, an axis refers to a direction or line along which a tool or workpiece moves. These axes allow the machine to manipulate materials precisely. The more axes a machine has, the more complex the operations it can perform, enhancing its flexibility and capability to create intricate designs.
For example, in a 2-axis machine, the tool moves in two directions, while a 5-axis machine can move along five different directions simultaneously, giving it much more freedom to craft detailed shapes.
| Axis | Direction of Movement | Key Functionality |
|---|---|---|
| X-axis | Left to Right (Horizontal) | Controls horizontal movement along the length of the material. |
| Y-axis | Front to Back (Horizontal) | Provides movement across the width of the material. |
| Z-axis | Up and Down (Vertical) | Controls depth for precise cutting and milling. |
As machines become more advanced, additional axes are added for greater flexibility and precision. At RBT Intelligent Equipment, we specialize in multi-axis CNC machines designed to deliver high-quality results, whether for aerospace or automotive applications.
CNC machines come in various configurations, each designed to handle different levels of complexity. The number of axes directly impacts how flexible and precise the machine can be. Let’s break down some of the common CNC configurations.
2-Axis CNC Machine
A 2-axis CNC machine can move the tool in two directions: left to right (X-axis) and up and down (Y-axis). It’s the simplest configuration, typically used for basic cuts and engraving. However, its limitations become apparent when dealing with more complex parts or deep cuts.
3-Axis CNC Machine
The 3-axis machine is the most common configuration. It adds vertical movement (Z-axis) to the left-right and front-back movements, allowing for more complex shapes. It’s perfect for tasks like drilling, milling, and cutting simple to intermediate parts. It offers good precision for most applications but may struggle with more intricate designs.
4-Axis CNC Machine
A 4-axis machine introduces a rotation axis (A-axis), adding the ability to rotate the workpiece. This is particularly useful for machining cylindrical parts, such as gears or round shapes. The extra axis improves precision and reduces the need to reposition the material, making it ideal for certain types of more complex machining.
5-Axis CNC Machine
A 5-axis CNC machine allows for simultaneous movement along five different axes: X, Y, Z, A, and B. This configuration provides high precision and flexibility, making it ideal for creating complex, free-form parts like turbine blades and medical implants. With 5 axes, the machine can work on multiple sides of a part at once, reducing setup time and increasing efficiency.
6-Axis CNC Machine
The 6-axis machine adds another rotational axis, typically C, allowing for even more intricate movements. This is particularly useful for parts that need more complicated geometries, such as aerospace components. The added axes make it ideal for high-precision applications, reducing the need for secondary fixtures.
7-Axis CNC Machine
A 7-axis machine takes precision to the next level. It’s capable of more movements for even more complex geometries. The seventh axis is often used for workpiece manipulation, providing flexibility in special industries like aerospace and automotive. With this many axes, the machine can handle the most complex designs.
9-Axis and 12-Axis CNC Machines
These highly advanced machines combine multiple rotational axes, giving them the ability to move in many directions simultaneously. This results in unmatched flexibility and precision. 9-axis and 12-axis CNC machines are used for manufacturing extremely intricate parts, such as medical devices and high-performance aerospace components.
Here's a quick look at the progression of CNC machine axes:
| Machine Type | Number of Axes | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| 2-Axis CNC | 2 | Simple cuts, engraving, flat surfaces |
| 3-Axis CNC | 3 | Milling, drilling, simple to intermediate parts |
| 4-Axis CNC | 4 | Cylindrical parts, rotating for precision |
| 5-Axis CNC | 5 | Complex parts, free-form designs |
| 6-Axis CNC | 6 | High precision, aerospace components |
| 7-Axis CNC | 7 | Complex geometries, specialized industries |
| 9/12-Axis CNC | 9-12 | Highly intricate parts, medical, aerospace |
At RBT Intelligent Equipment, we offer advanced CNC machines, including multi-axis models, designed to provide precision, speed, and flexibility for industries like aerospace and automotive.

Precision:
More axes allow the CNC machine to make more precise cuts from various angles. With 3 axes, the machine can move along the basic planes, but with 5 or more axes, it can handle intricate details and compound cuts with much higher accuracy. The added freedom of movement helps reduce errors during the machining process.
Complexity of the Parts:
When designing complex parts, such as turbine blades or custom medical implants, more axes are essential. Machines with 5 or more axes can cut multiple sides of the part simultaneously, eliminating the need to reposition the workpiece. This is crucial for parts with complex geometries and angles.
Time Efficiency:
More axes can reduce machining time by allowing the machine to complete multiple tasks at once. Instead of repositioning the material multiple times, the machine can approach the part from various angles, which speeds up production. A 5-axis machine, for instance, can reduce overall machining time compared to a 3-axis machine by handling more complex cuts in a single setup.
Simple Tasks:
For basic tasks like drilling or milling flat surfaces, a 2 or 3-axis CNC machine is sufficient. These machines are ideal for simple parts like brackets, washers, and other components with straightforward geometries.
Complex Parts:
For intricate designs or parts that require cutting on multiple surfaces, a 5-axis or more advanced machine is necessary. Aerospace, automotive, and medical industries often rely on 5-axis CNC machines to create precise, complex shapes. These machines handle detailed cuts without the need for repositioning the part.
Cost Considerations:
While more axes provide better precision and speed, they come at a higher price. A 2-axis machine is much more affordable than a 5-axis machine, but it can’t handle as many complex tasks. When choosing the right machine, consider the complexity of your parts, your budget, and the desired precision. It’s crucial to balance cost and the capabilities you need for your project.
Here’s a quick comparison of the most common CNC machine types:
| Machine Type | Number of Axes | Ideal Use Cases | Approximate Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-Axis CNC | 2 | Simple cuts, flat parts, engraving | Low to Mid-range |
| 3-Axis CNC | 3 | Milling, drilling, moderate complexity parts | Mid-range |
| 5-Axis CNC | 5 | Complex parts, free-form designs, aerospace | High-range |
| 7-Axis CNC | 7 | Highly complex geometries, aerospace, automotive | Premium |
2-axis CNC machines are perfect for simple tasks. They’re used to make flat objects, basic cuts, and engravings. Industries like sign-making and decorative parts often use them. They’re also ideal for producing flat, prismatic shapes such as brackets, washers, or simple housings.
The 3-axis CNC machine is a workhorse in many industries. It’s commonly used for milling, drilling, and cutting simple parts. These machines are widely employed in automotive and manufacturing industries, where they create components such as gears, frames, and small mechanical parts. Their ability to move along three axes makes them perfect for moderate complexity tasks.
4-axis CNC machines excel in tasks requiring rotation along a cylindrical shape. They are used for cutting holes, grooves, or slots in cylindrical parts. Industries like aerospace and automotive use them to produce parts like shafts, cams, and complex rotary components. The added rotational movement increases precision and efficiency in these operations.
The 5-axis CNC machine is essential in industries requiring high precision and complex parts. It’s used to create medical components, aerospace parts, and complex engineering designs. For example, it’s often used to manufacture turbine blades, custom prosthetics, or aerospace components, where multi-directional cuts are needed. The ability to approach the part from multiple angles reduces setup time and increases accuracy.
6-axis and more advanced CNC machines are used for ultra-precise applications in aerospace, automotive, and military industries. These machines are capable of producing intricate designs like turbine blades, aircraft components, or missile parts, where high accuracy is essential. With their enhanced movement capabilities, these machines can create highly complex parts without multiple setups, improving production speed and part precision.
Here’s a quick breakdown of applications by CNC machine types:
| CNC Machine Type | Common Applications |
|---|---|
| 2-Axis CNC | Simple, flat objects, engraving, basic cuts |
| 3-Axis CNC | Milling, drilling, cutting basic parts (automotive, manufacturing) |
| 4-Axis CNC | Cylindrical parts, cutting grooves, slots |
| 5-Axis CNC | Medical components, aerospace parts, engineering designs |
| 6-Axis CNC | Aerospace, automotive, military, complex designs |
Part Complexity:
The complexity of the part you’re producing should guide the choice of CNC machine. For simple parts like brackets or washers, a 2-axis or 3-axis machine is enough. But for more intricate parts such as turbine blades or aerospace components, a 5-axis or higher machine is required. More axes allow for more angles of precision and efficiency, reducing setup times.
Material Types:
Different materials require different types of machines. Soft materials like plastics and aluminum can be easily handled by 3-axis CNC machines, while harder materials like steel may require machines with more axes to ensure precision and avoid wear. For composite materials, more advanced machines with higher flexibility may be necessary to handle the unique cutting requirements.
Budget and Cost-Benefit Analysis:
The cost of a CNC machine increases with the number of axes. While a 2-axis or 3-axis machine is more affordable, it may not be suitable for complex or intricate tasks. Consider the long-term returns on investment when deciding. If your business requires precision and high complexity, investing in a 5-axis machine may be worthwhile despite the higher upfront cost. Always balance your budget against the expected efficiency and quality.

Technological Advancements in CNC Machining
CNC machines continue to evolve with emerging technologies. Artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are becoming key players, optimizing tool paths and reducing human error. These advancements promise faster production speeds, greater precision, and improved flexibility. Integration of additional axes is expected to further enhance the capabilities of CNC machines.
The Rise of Hybrid Machines
Hybrid machines, which combine 3D printing with traditional CNC machining, are gaining popularity. These machines offer enhanced flexibility, allowing manufacturers to print parts and then finish them with precision machining. This combination helps create more complex parts while maintaining high precision and reducing production times.
Understanding the number of axes in a CNC machine is essential for precision and production efficiency. More axes allow for greater flexibility and accuracy, especially for complex designs.
When choosing a CNC machine, consider part complexity, material types, and your budget. For intricate projects, investing in a multi-axis machine is often worthwhile. At RBT Intelligent Equipment, we offer a range of CNC machines designed for various industry needs, ensuring high-quality results and improved efficiency.
A: A 3-axis CNC machine moves in three directions (X, Y, Z), while a 5-axis machine adds rotational movement (A and B axes). The 5-axis machine allows for more complex cuts, reducing setup time and increasing precision.
A: If your project involves cylindrical parts or simple rotations, a 4-axis machine may be enough. For more intricate geometries or multiple angles, a 5-axis machine is needed.
A: No, a 2-axis CNC machine is ideal for simple cuts and flat parts but lacks the flexibility required for complex designs.
A: Aerospace, automotive, and medical industries benefit from 5-axis and 7-axis machines, as they require high precision for complex, intricate parts.
A: Switching to a 5-axis machine may require new software configurations and tools, as the added axes involve more complex programming and setups.